Back to blogs
Whether you’re a talent acquisition veteran or new to recruiting, you likely can relate to the struggle of creating effective Boolean search strings. Boolean search in recruitment is a must-have skill to develop a winning sourcing strategy and to be known as a true talent advisor in your organization—but Boolean does take a little practice to perfect.
In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of using Boolean search to help you work more efficiently and find the right pool of candidates to fill open roles. We’ll show you a few advanced Boolean search techniques for recruiters and some that are specific to SeekOut.
What is Boolean search?
Boolean search is an online search technique that's used to help you generate quality, precise results. By writing Boolean search strings—which are made up of key phrases alongside words and symbols called operators (e.g., AND, OR, NOT)—you can perform nuanced, multi-layered searches to widen or narrow your results so that you can find exactly what you’re looking for.
Here’s an example of what a Boolean search string looks like:

In recruitment, Boolean search is used to sort through thousands of candidates to source only those who match a particular job description. Boolean searches can be performed in databases (e.g., Google, LinkedIn, SeekOut), your applicant tracking system (ATS), and job portals.
Why Boolean search in recruitment is worth mastering
Boolean does require some practice to master, but the benefits of learning it will make all the difference in your role as a recruiter.
You’ll have complete control of your searches
With Boolean search, you’re giving the database a specific, customized set of instructions to find the results you want. You're “telling” the database what to do (i.e., what results you want to see).
Compare this to search engines like Google, where you’re using everyday language in the form of keywords or a question to conduct a search. An algorithm will bring you results from sources all over the web that it thinks you may find helpful (i.e., it’s taking its best guess to determine what you’re looking for). Boolean, on the other hand, only brings you results that match the exact parameters you’ve set in your search string.
You’ll leverage databases much more effectively
Boolean is an effective way to use a database to its fullest potential. Many databases have pre-built search filters or a primitive search bar, but these can sometimes limit your ability to be as specific or accurate as you want.
Learning Boolean search recruiting is like uncovering a hack within the search platforms you’re already using, allowing you to find much more targeted and accurate search results.
You'll find the right candidates faster
Instead of sorting through thousands of candidates who may or may not be the right fit for an open role, Boolean search gives you a more precise pool of qualified candidates to choose from. You'll save time by looking only at candidates you know are the best fit.
The basics of Boolean search in recruitment: 5 operators you should know
If you’re new to Boolean search in recruitment, this section serves as an overview of the basics you should commit to memory. The following Boolean operators will help you build effective search strings, and they'll work across any database you use.
1. AND (Narrow your search)
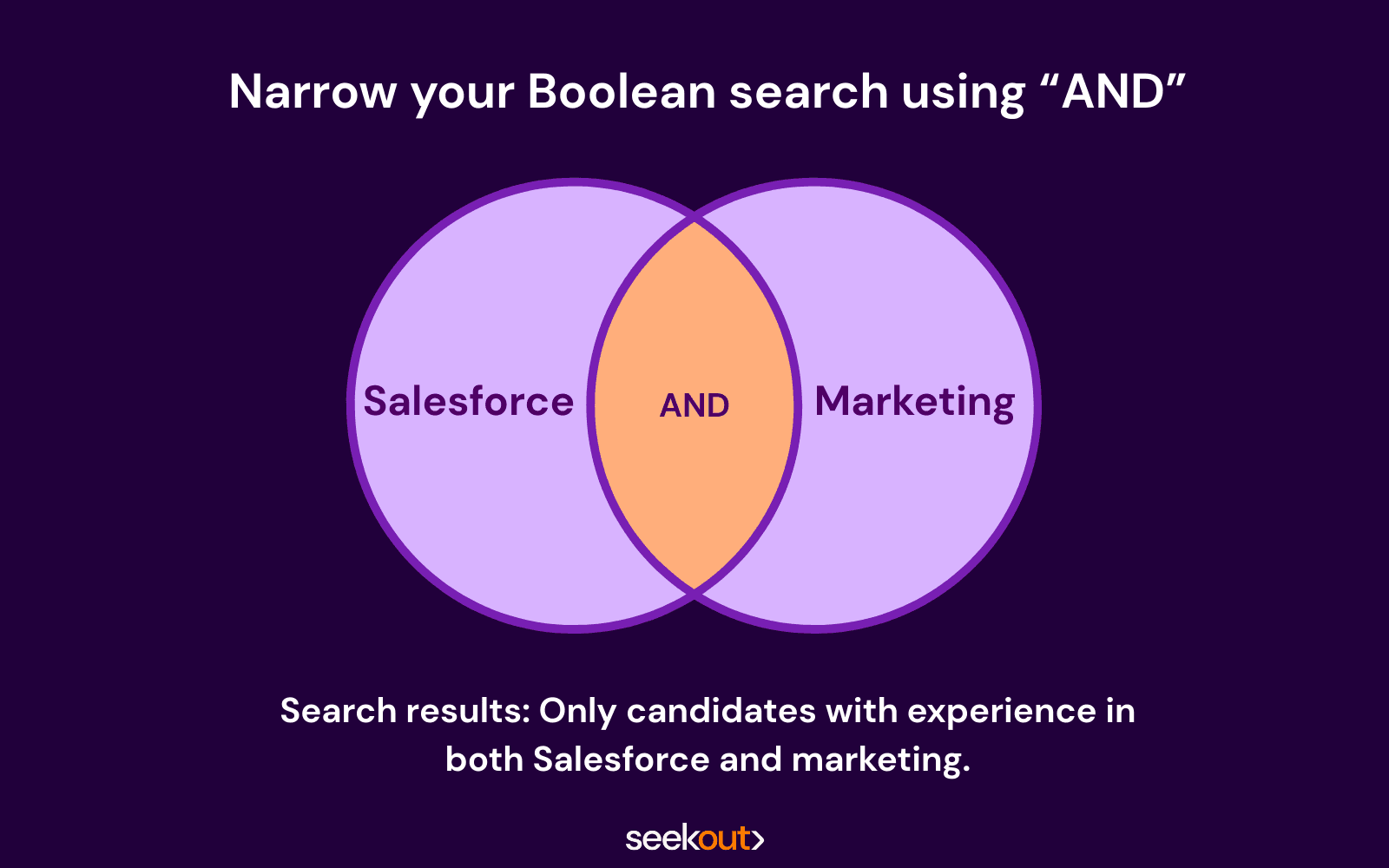
How it works: The AND modifier will narrow your results by adding more requirements to the search. Use AND to drill down a large number of candidates to the ones who best meet your job requirements.
As an example, we’ll use the AND operator to help us find candidates who have marketing and Salesforce experience.
Boolean search recruiting example with AND: marketing AND salesforce
What you’re telling the database to do: The words “marketing” and “Salesforce” need to be present for each candidate who shows up in your results.
2. OR (Expand your search)
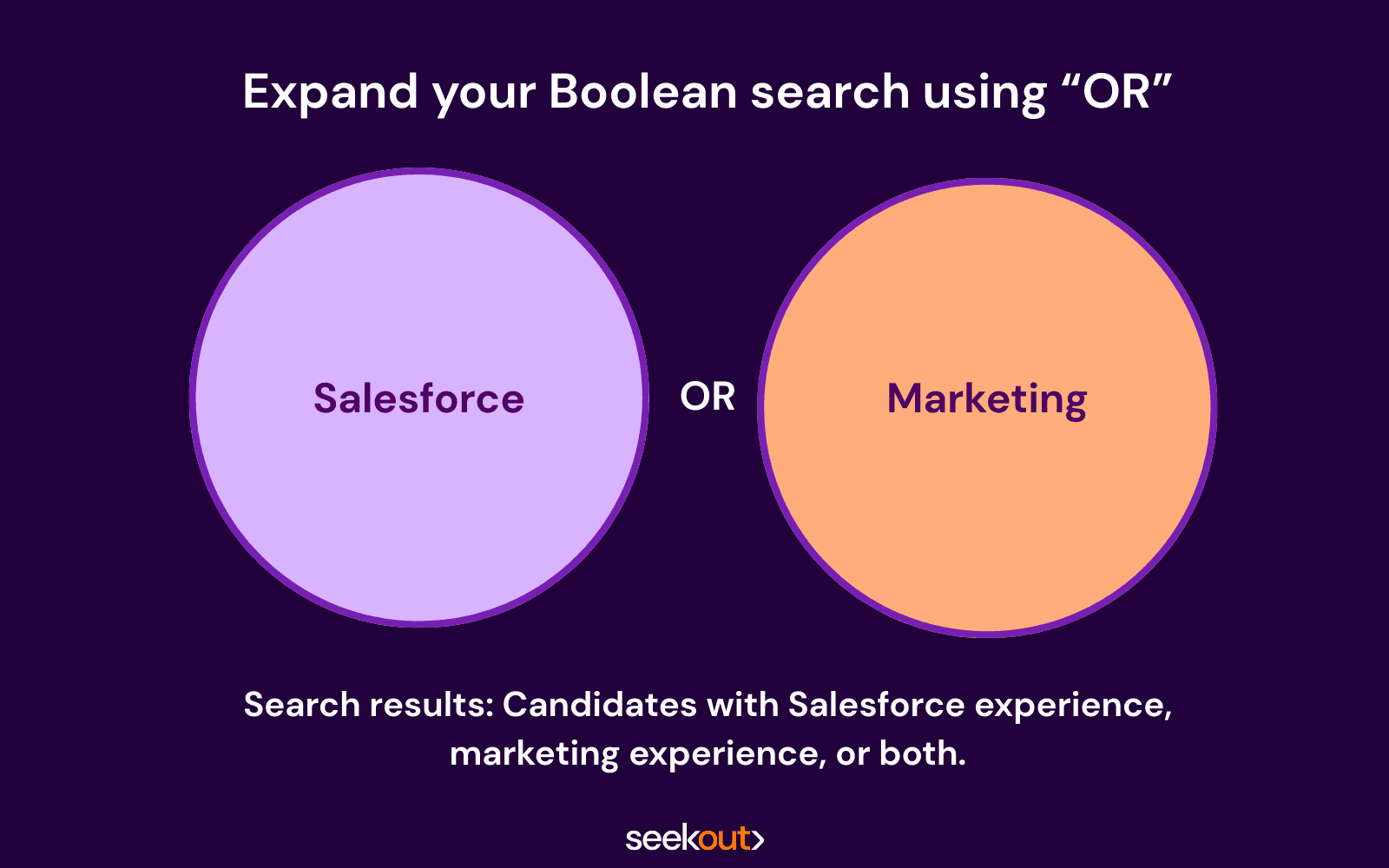
How it works: The OR modifier does the exact opposite of AND—instead of narrowing down the search, it expands it.
As an example, we’ll use the OR modifier to find candidates who mention Salesforce or Hubspot experience.
Boolean search recruiting example using OR: salesforce OR hubspot
What you’re telling the database to do: Show me candidates with either “Salesforce” or “HubSpot” present.
3. Parentheses (Prioritize specific terms first)
How it works: Parentheses—sometimes called brackets—are crucial to Boolean recruiting because they let the database know your order of operations (i.e., which parts of your search string to prioritize).
Parentheses tell the database what is an OR versus what is an AND. Not using parenthesis or even using them in different parts of your search string can yield very different results.
These two examples illustrate how impactful parentheses are to your search results.
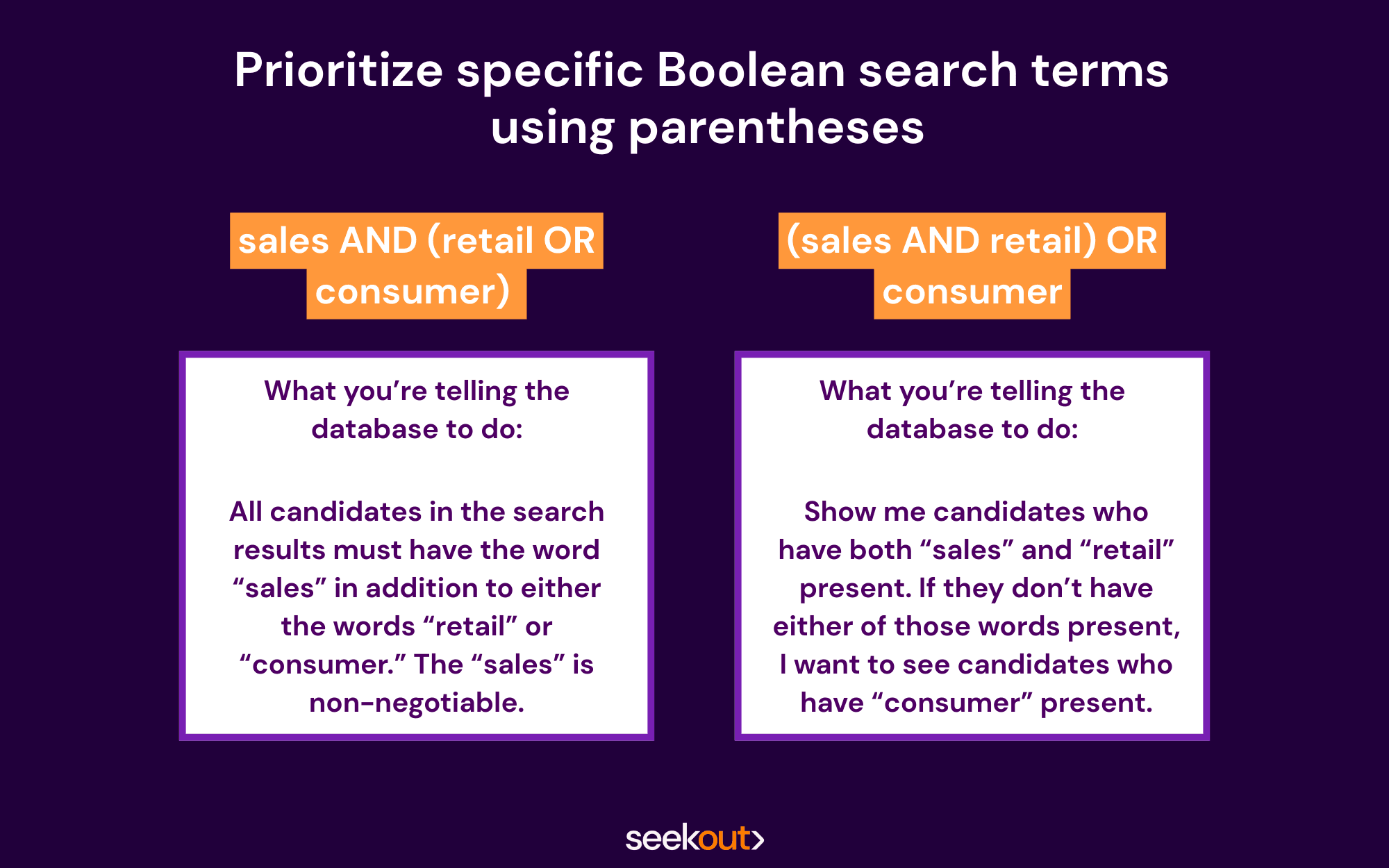
Boolean search recruiting example with parentheses: sales AND (retail OR consumer)
What you’re telling the database to do: All candidates in the search results must have the word “sales” in addition to either the words “retail” or “consumer.” The “sales” is non-negotiable.
Now, switch the parentheses around in the example above to the following: (sales AND retail) OR consumer
What you’re telling the database to do now: Show me candidates who have both “sales” and “retail” present. If they don’t have either of those words present, I want to see candidates who have “consumer” present.
Tip: All OR statements should be in a set of parentheses. |
|---|
4. Quotation marks (Group words together)
How it works: Quotation marks are needed to search for phrases of two or more words to return an exact match. By putting quotation marks around a group of words, you're telling the database to bring back results that have this exact phrase written this exact way. If you don’t use quotation marks around a group of words, the search engine won't locate those words in that exact order, which can lead to undesired results.
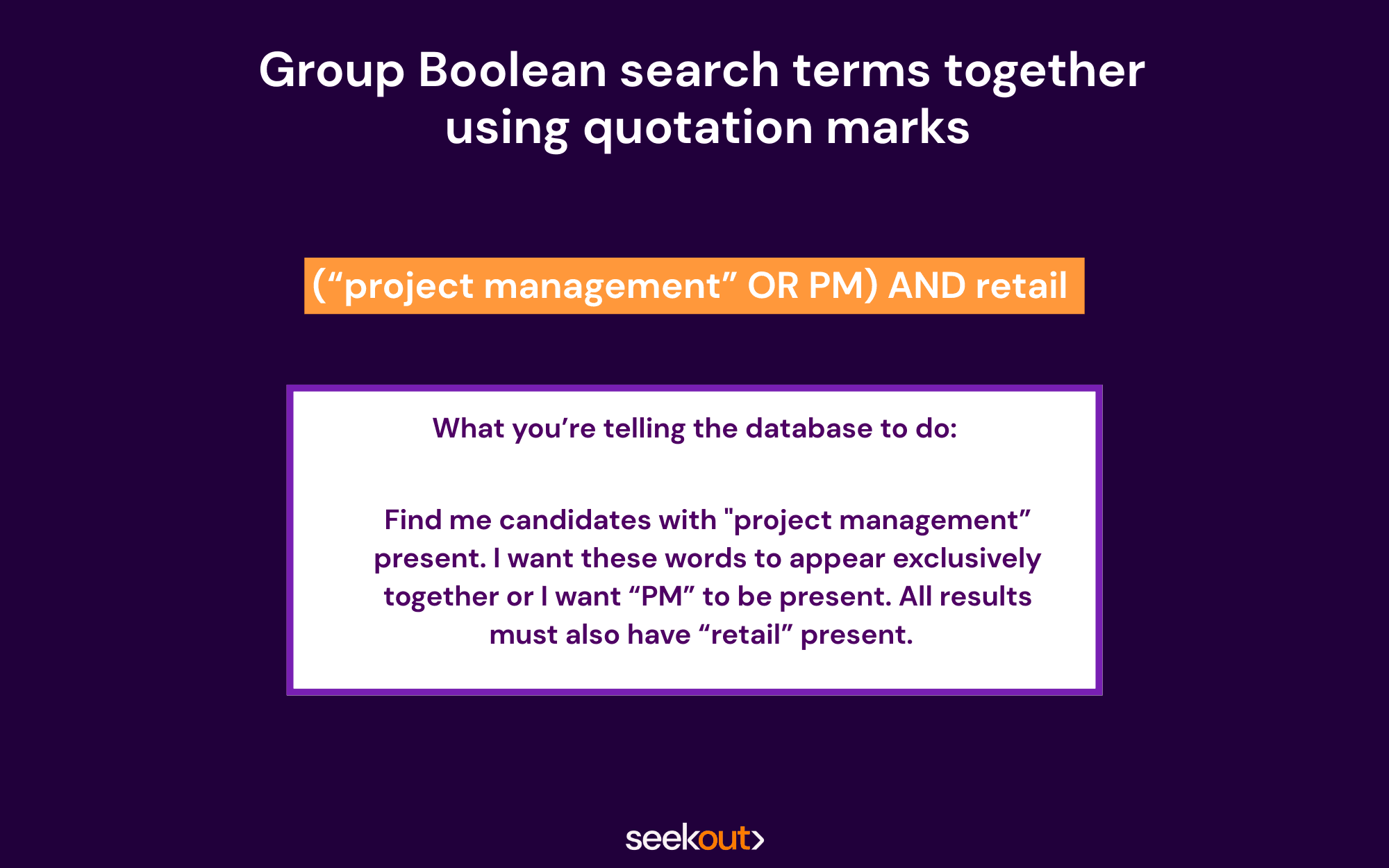
Boolean search recruiting example using quotation marks: (“project management” OR PM) AND retail
What you’re telling the database to do: Find me candidates with "project management” present. I want these two words to appear exclusively together or I want "PM" to be present. All results have to have “retail” present.
If you hadn’t used quotation marks around “project management,” the search would bring up results that had both “project” and “management” included anywhere on the page—not necessarily the phrase “project management” together.
Tip: Quotation marks are not required for single words. Any phrases with two or more words should be in quotes. |
|---|
5. NOT (Exclude terms from your search)
How it works: The NOT modifier excludes specific terms from appearing in your search results.
Say you want to avoid candidates who work at a specific company because you have a non-solicitation agreement with them. We'll use the operator NOT to hide candidates who have worked with Uber from your search.
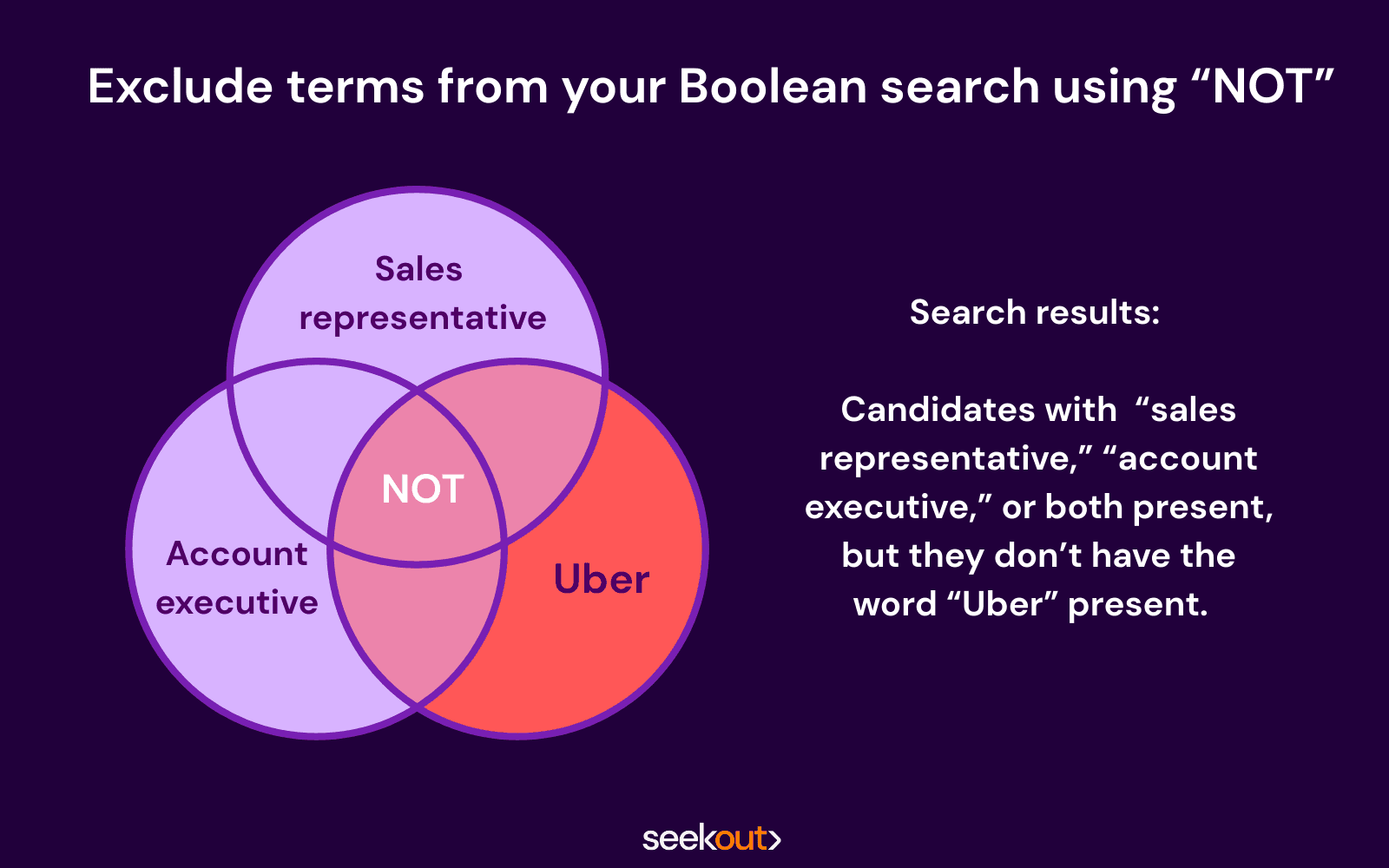
Boolean search recruiting example using NOT: (“sales representative” OR “account executive”) NOT Uber
What you’re telling the database to do: Show me candidates with either “sales representative” or “account executive” phrases present or both, but they don’t have the word “Uber” present.
Advanced Boolean searches for recruiters
Once you’ve mastered the basic Boolean sourcing techniques above, you can start playing around with more advanced operators. As we mentioned before, the previous five operators will work across any database. Advanced operators, however, may not work universally, or they’ll work a little differently depending on the database’s syntax. There are many advanced Boolean operators you could use, but here is a simple option to get you started.
6. SITE: (Search within a specific website)

If you’re setting up a Boolean search in Google, this operator will come in handy to scan specific websites for candidates, such as a portfolio website like Dribbble.
How it works: When you add the SITE: operator to the beginning of your Boolean search string, you'll need to add the exact website you want to search within immediately after it (don’t leave a space) along with your search criteria.
Boolean search recruiting example using SITE: SITE: dribbble.com (brand AND design) Seattle
What you’re telling the database to do: Conduct the following search within the dribbble.com website: candidates with both brand and design experience who live in Seattle.
See “Field Search” in the following section to see how this is done in the SeekOut platform.
Boolean search in recruitment using SeekOut
SeekOut makes Boolean for recruiters easy because it offers flexible options that take the guesswork out of building long search strings. Not only does SeekOut make Boolean sourcing less of a hassle, but we give recruiters more accurate search results thanks to our AI-powered search engine that taps into hundreds of millions of candidates across the web (including LinkedIn and GitHub) and brings them all into one platform. You’ll see each candidate in their own comprehensive profile, highlighting the exact (or similar) experience you’re looking for, not just matching keywords.
Here are several simple ways you can conduct Boolean sourcing in SeekOut. (Note: These operators work differently in SeekOut versus other databases).
Field search
How it works: Field Search operators help narrow down your search results by limiting the search to specific fields versus scanning for the word across an entire profile. Field Search helps you target things like current and past job titles, current and past companies, or skills (just to name a few).
For a complete list of SeekOut’s Field-based searches see our Help Page.
Boolean search example in SeekOut: cur_title:“software engineer” AND skills:(java AND python)
What you’re telling SeekOut to do: Limit my search of “software engineer” just to a candidate’s “current title” and search for “Java” and “Python” within the “Skills” field specifically.
You’ll likely have fewer results than if you were to perform a similar search in another database, but you can trust that the candidates who do come through will be high quality.
Wildcards (vary a keyword)
How it works: Wildcard looks for variations of a keyword to create a broad-reaching search string. This operator is an efficient way to search when you have terms that have lots of variations (e.g., engineer and engineering) and ensures that you are getting the most inclusive search possible.
The wildcard operator can be in the form of an asterisk (*) or question mark (?) depending on the database you’re using (if you’re a SeekOut user, the platform supports both).
Boolean search recruiting example with wildcard: writ* AND edit*
What you’re telling the database to do: Find me candidates with both writing and editing words present, including any variations of those keywords: writer, writing, written, etc. and editor, editing, edited, etc.
For SeekOut users, the asterisk is a placeholder for multiple letters and the question mark is a place holder for a single letter. So, stor? would deliver results for story, stork, storm, etc.
The Wildcard thinks of every variation of a word so you don’t have to. It saves you from writing long search strings.
Proximity
How it works: SeekOut’s proximity operator uses a tilde (~) to perform proximity searches that look for keywords near each other but not directly next to one another on a candidate’s profile.
Boolean search example in SeekOut using Proximity: cur_title:“senior engineer”~1
What you’re telling SeekOut to do: Find candidates who have “senior” and “engineer” in their current titles within one word of each other.
Your results would include candidates with titles such as “Senior software engineer,” “senior systems engineer,” and “senior design engineer.”
For a complete list of the advanced Boolean searches you can use in SeekOut, check out our help page.
Alternatives to Boolean search in SeekOut
SeekOut offers a few different ways to conduct a search without having to manually type out Boolean search strings.
SmartMatch
How it works: If you’re new to Boolean or just want to conduct faster searches, you’ll love SmartMatch. With SmartMatch, you can skip writing out Boolean search strings and get straight to the search results with just a few clicks.
In the SmartMatch field, select the job titles, required skills, and preferred skills that best fit your job description. SeekOut will suggest related skills and titles to improve your search. And you can even choose to exclude certain titles or skills to ensure you have the most relevant candidates in your pool.
SeekOut Assist
How it works: SeekOut assist takes AI recruiting to a new level. Instead of spending time writing out a Boolean search string, SeekOut Assist will create a search for you almost instantly.
Copy and paste your job description and SeekOut Assist automatically generates a targeted search and then lists the most qualified candidates for your role.
As a bonus, once you’ve found a candidate you’d like to reach out to for an open role, SeekOut Assist creates a personalized outreach message that’s unique to their interests, skills, and qualifications.
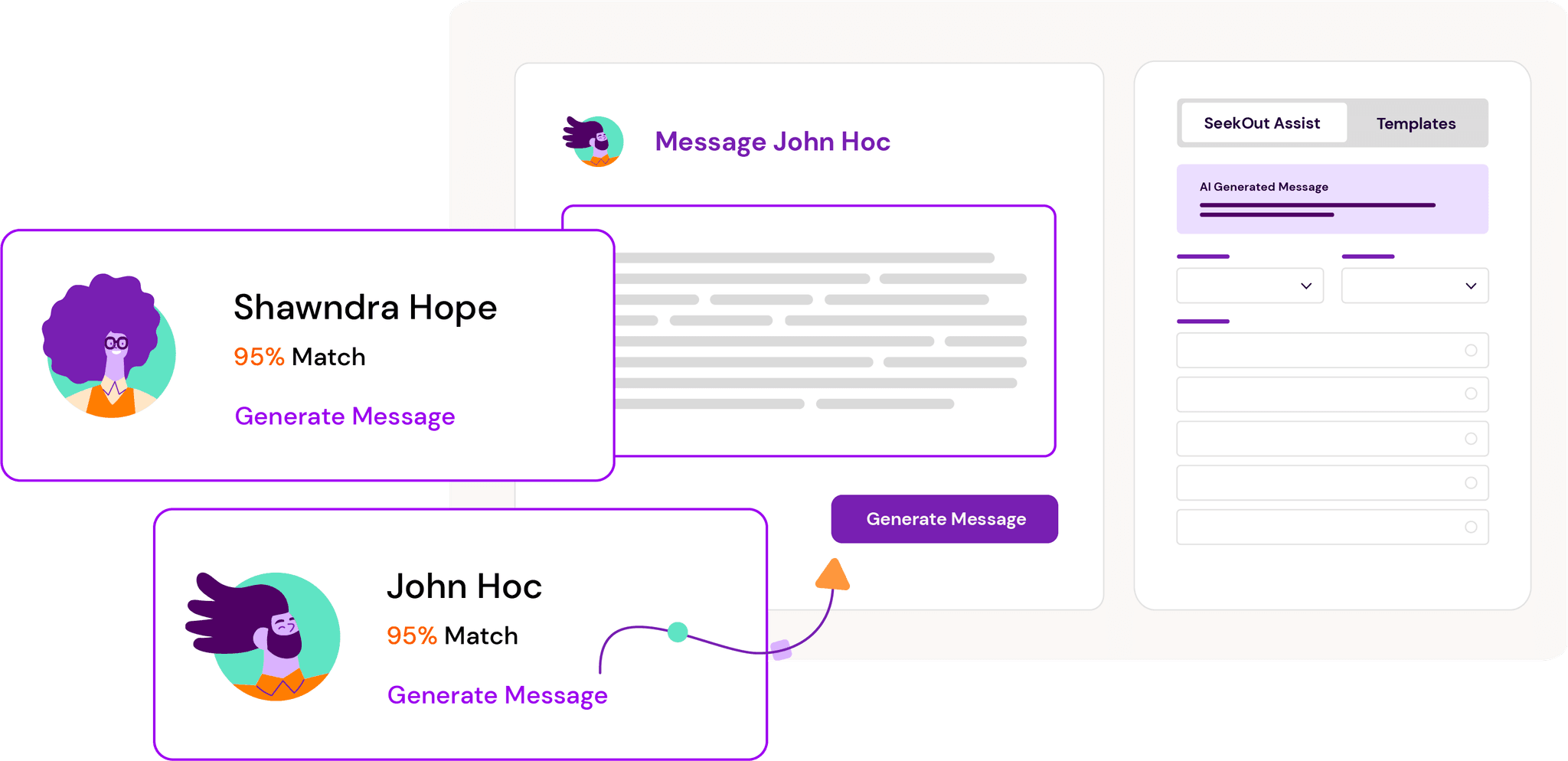
Watch: See SeekOut Assist and SmartMatch in action
Additional pro tips when using Boolean search in recruitment
Use ChatGPT to help you brainstorm and draft search strings. For brainstorming, you could ask ChatGPT to help you think of alternative job titles for a certain role or identify common skills for a role in an industry you’re not familiar with. ChatGPT can also help you write out lengthy Boolean strings with just a few sets of criteria. Just be sure to modify the string based on your specific needs and the platforms you’re using for candidate sourcing. Read our ChatGPT Recruiting guide.
Save your commonly used search strings. If you find yourself using the same search strings again and again, save them in a file on your desktop so you can copy and paste them into your database. If you’re a SeekOut user, you can save searches directly to your account.
Practice, practice, practice. To get better at Boolean sourcing, it’s essential to give yourself time to practice and learn how Boolean can best be used to find the candidates you’re looking for. Watch the webinar "A Beginner's Guide to Boolean Search" for more examples.
Read this next: 10 ChatGPT Prompts for Recruiters
Download nowSee us in action
Learn how SeekOut unifies people data to help organizations reach their talent goals
Request a demo